Glass, a Material for Sustainable Development
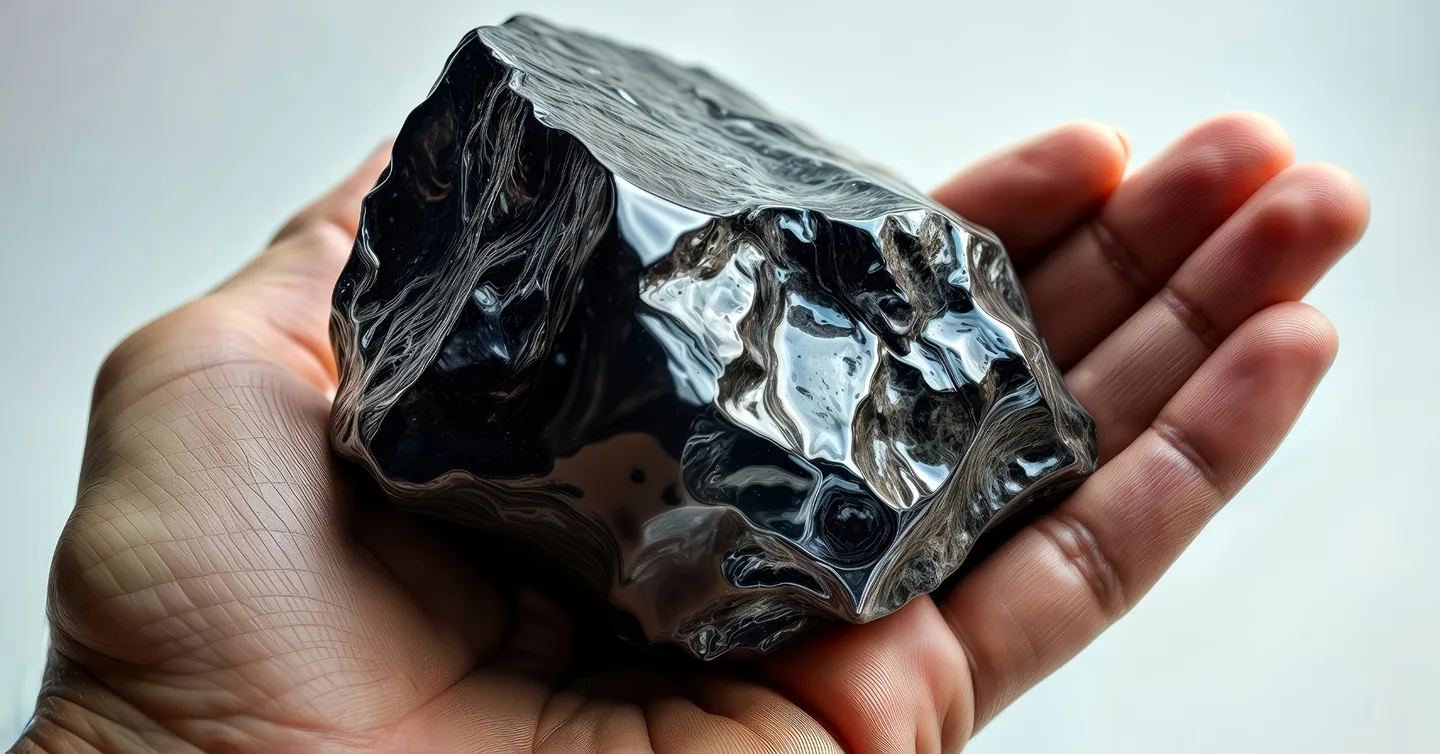
Photo : Obsidian, a glassy stone formed by a volcanic eruption. The material was useful for making tools in the Stone Age.

- • How is glass different from microplastics?
- • Harmony with the Earth
- • Glass, the determining factor in the invention of Edison’s light bulb
- • History of glass dating back to around 4000 to 5000 BC
- • Create “products recognized as the very best of human civilization”
- • New functions needed by society
- • NEG’s special glass helping attain the SDGs
- • Production of renewable energy
- • All-solid-state sodium-ion secondary batteries
- • New challenges to attain the SDGs
How is glass different from microplastics?
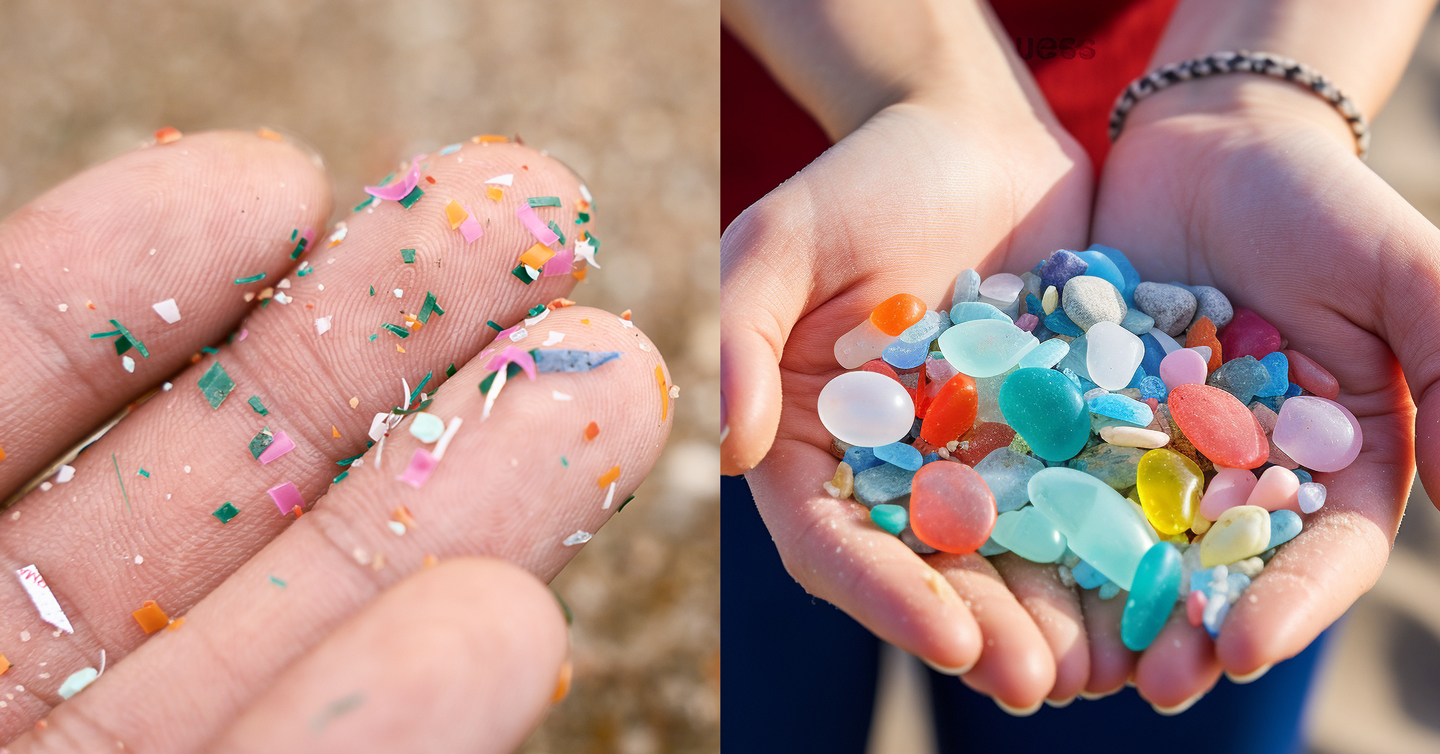
As you know, large amounts of plastic waste floating in the sea have emerged as an issue toward achieving the SDGs (Sustainable Development Goals). In addition to large items of plastic waste, such as plastic bags and bottles discarded on land and in the sea, the problem of microplastics, which are tiny fragments of such plastic waste, has attracted much public attention recently.
Do you remember going to the seaside and picking up colorful and shiny glass pieces on a beach? Known as “sea gems,” “sea glass,” or “beach glass,” they are collected by families with children and used for artworks by some people. Originally, they were broken pieces of empty glass bottles or glass floats used as fishing gear. While being tossed by the waves and exposed to rocks and sand, their edges were rounded, and they washed up on sandy beaches.

Harmony with the Earth
“While microplastics have become a major social issue, no one cares about glass. People pick up colorful pieces of sea glass on beaches. Notably, pieces with rare shapes and colors are treated like gems. This is because glass is a material in profound harmony with the Earth. Components of general glass are almost the same as those which make up the ground surface. Because glass is made by melting these components at high temperature, the risk of environmental pollution and the impact on the ecosystem are considered minimal. Sea glass on beaches is weathered by waves and sand and eventually return to the Earth. Glass containers can withstand long-term use and barely deteriorate. In Europe, where environmental awareness is particularly high, reuse is commonplace, and a recycling system has also established.”
This explanation was given by Senior Vice President Hiroki Yamazaki of Nippon Electric Glass (NEG).

As for recycling, the same type of glass is a valuable raw material for NEG, a glass manufacturer, so it is melted in a melting furnace and reused to manufacture products. Given that the use of recycled glass contributes to reducing consumption of natural raw materials and energy, glass is a material highly harmonious with the environment.
In terms of sustainable development, glass has played an important role in the development of human civilization. Glass is considered one of the oldest man-made materials. It has been used in all aspects of society to enrich our lives.
Reference: An educational material released by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology “One S&T Poster for Every Household: Glass — THE MOST UNIVERSAL MODERN MATERIAL”
Now, let’s take a look at the roles of glass, which has contributed to the development of society.
Glass, indispensable for the invention of Edison’s light bulb

History of glass dating back to around 4000 to 5000 BC
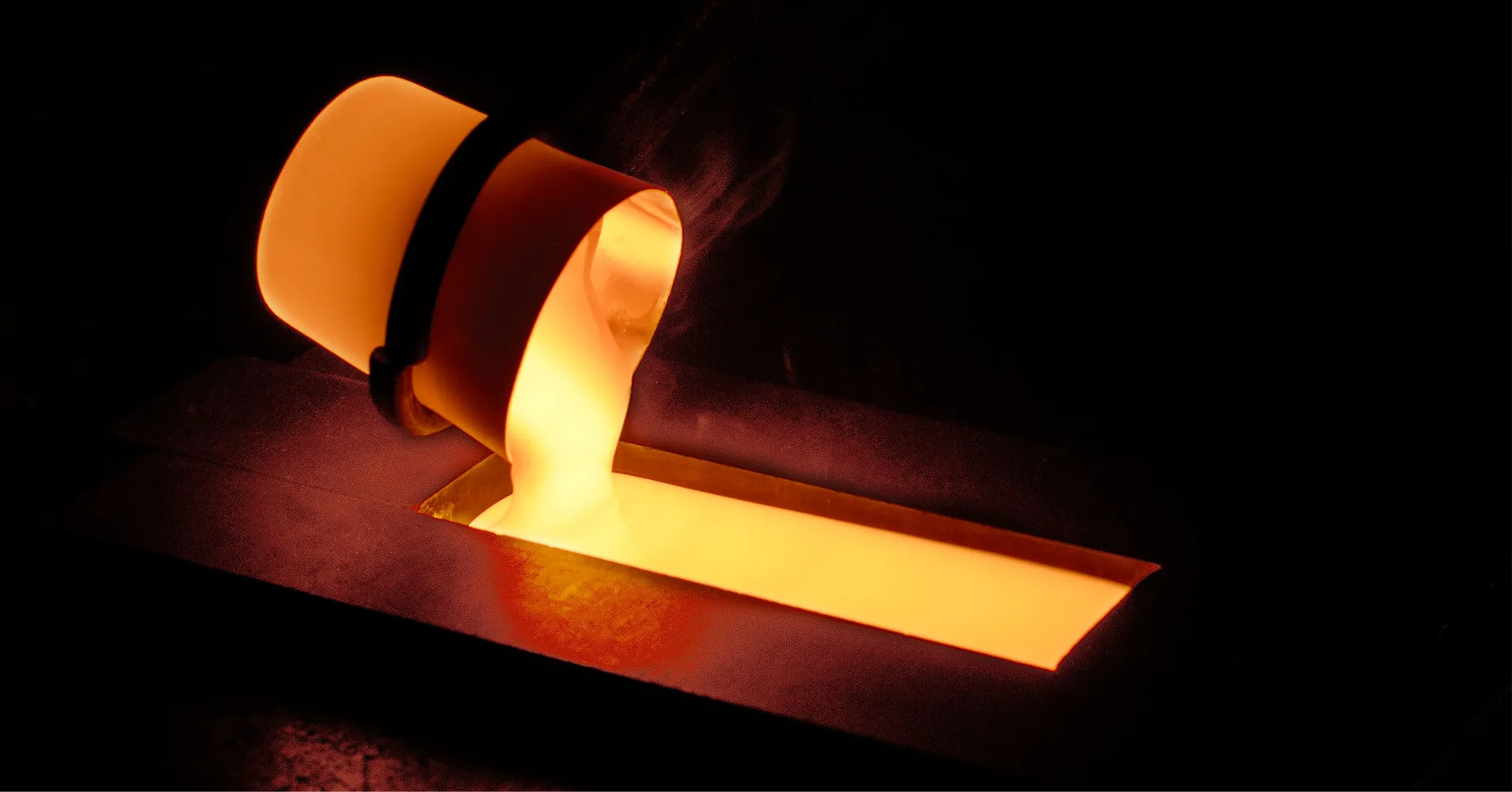
The history of glass dates back to around 4000 to 5000 BC. Glassmaking is considered to have started in Mesopotamia and Egypt. Around the 1st century BC, the glassblowing technique invented in ancient Syria enabled mass production of glass containers. Glass manufacturing technology evolved with the times. Glass with various shapes, properties, and functions appeared one after another, leading to a myriad of applications.
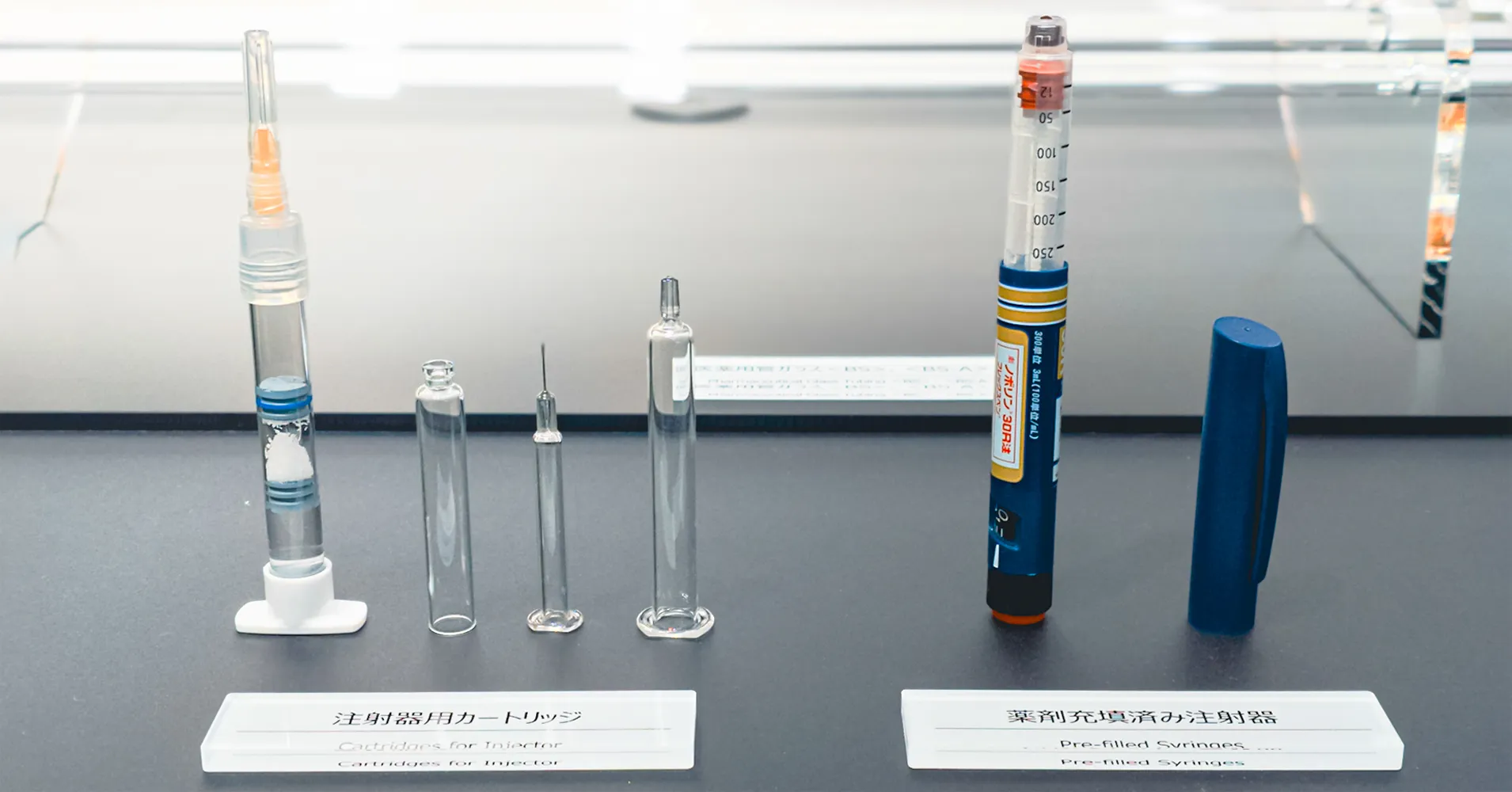
Yamazaki “For example, the technology developed by humans to make glass containers was subsequently applied to pharmaceutical containers. Window glass for buildings evolved into windows for mobility solutions, such as automobiles and trains. Eyeglass lenses evolved into telescopes and microscopes, laying the foundation for the development of astronomy and biology. The light bulb invented by Edison would have been impossible without glass. Later, it evolved into vacuum tubes and cathode ray tubes, leading to the subsequent development of various electronic devices and display devices. Nowadays, glass is also used for displays for smartphones and tablets as well as optical fibers for Internet communication. A multitude of examples demonstrate that glass plays a significant role in the development of society.”
Create “products recognized as the very best of human civilization”
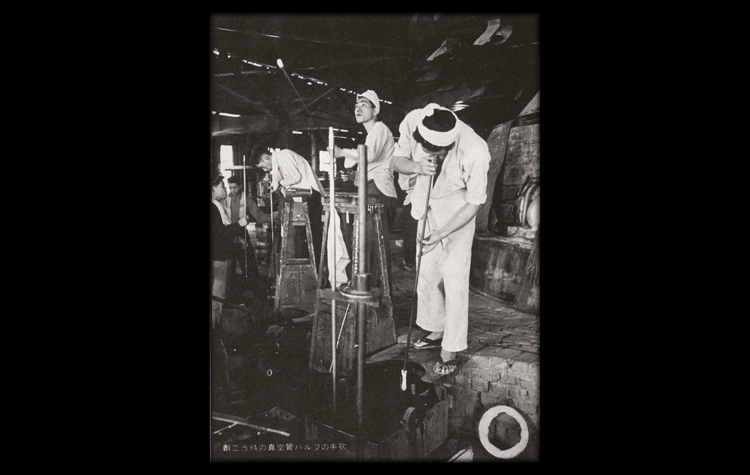

There is a message that is still embraced across NEG. It is “Create ‘products recognized as the very best of human civilization’,” which Junichi Nagasaki, the third president and de facto founder of NEG, always told to each of NEG people. Such products benefit us as time passes and grow with the progress of civilization. In other words, this is an admonition not to work on products that go against the flow of civilization.
New functions needed by society
Yamazaki “What we are trying to do is to realize new functions needed by society through special glass. For example, glass that shields radiation, which is harmful to the human body, is used in medical settings to protect the health of radiologic technologists, who operate X-rays and CT scans. Glass that does not break even when the temperature is rapidly raised or lowered is used for the top plates of induction cooking heaters and fire-rated windows for public facilities to prevent breakage and enable safe evacuation in the event of a fire. We constantly consider how we can create nice-to-have functions of glass and contribute to the realization of products recognized as the very best of human civilization. The functions sought by the advancement of civilization change rapidly with the times. We aim to ensure that the glass developed by us offer these functions to make people’s lives better. In fact, it is difficult to notice in our daily lives, but our glass is used in various ways as different parts, which cannot be seen from outside, in all kinds of products. That is, most people ‘use’ our glass without even realizing it.”
NEG’s special glass helping attain the SDGs
NEG’s efforts to attain the SDGs go beyond environmental measures, such as carbon neutrality and recycling. Our glass contributes to the realization of a sustainable society in various ways. Here are some examples.
Energy savings through weight reduction
For example, glass fiber reinforced plastic (GFRP), a composite material made of a highly functional resin reinforced with glass fiber, contributes to reducing the weight of automobiles. Replacing metal parts with GFRP reduces the weight of the automotive body and improves fuel efficiency. Electric vehicles (EVs), which are increasingly replacing internal combustion engine vehicles, pose a challenge in terms of the heavy weight of the body. GFRP is expected to assume a more prominent role in the future in further reducing the weight of EVs.
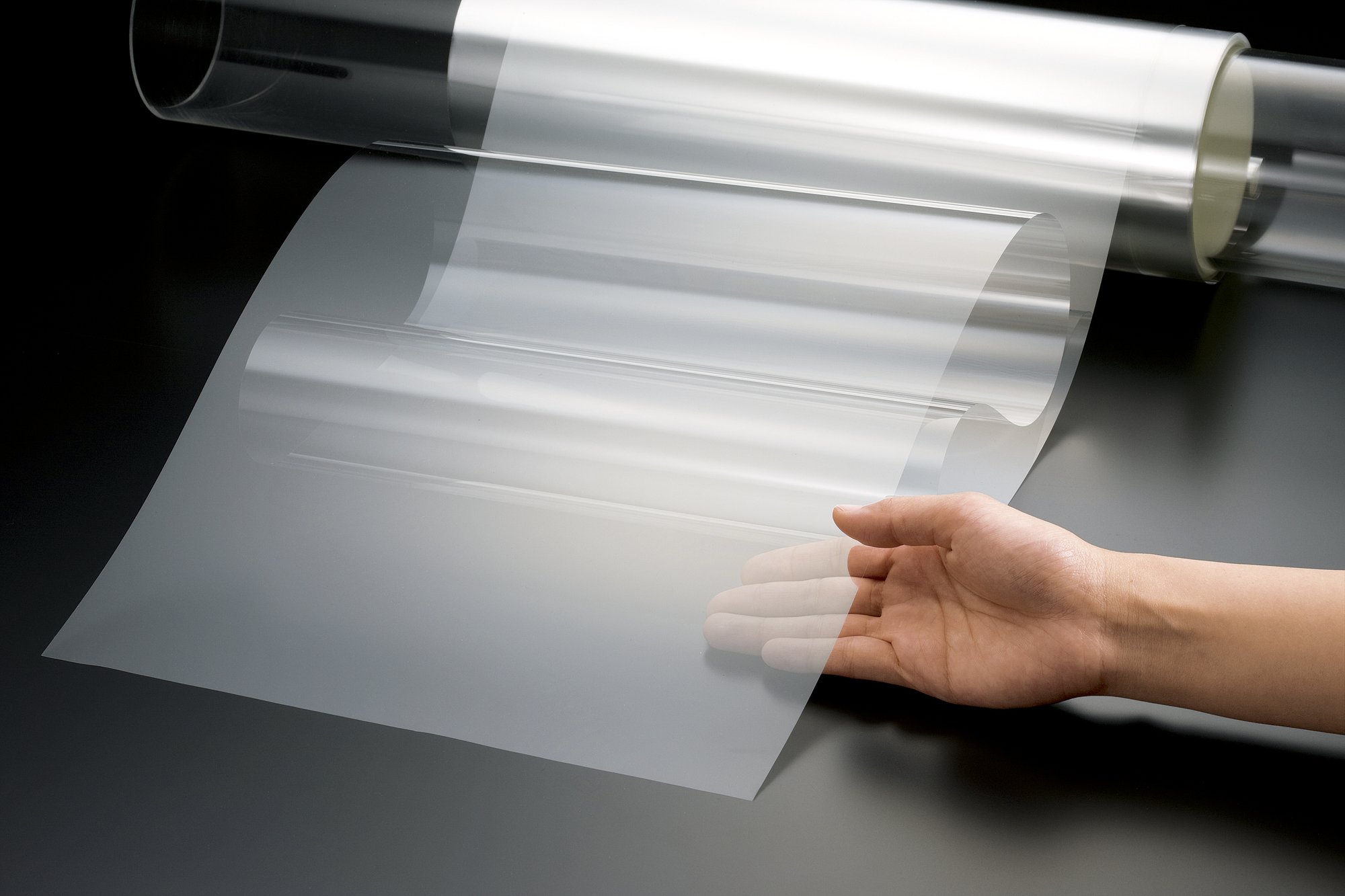
Reduction of the thickness of glass for displays while maintaining its strength makes it possible to reduce the external dimensions and weight of devices. This is expected not only to increase convenience for users but also to reduce logistics costs and the energy required for delivery. Ultra-thin Glass

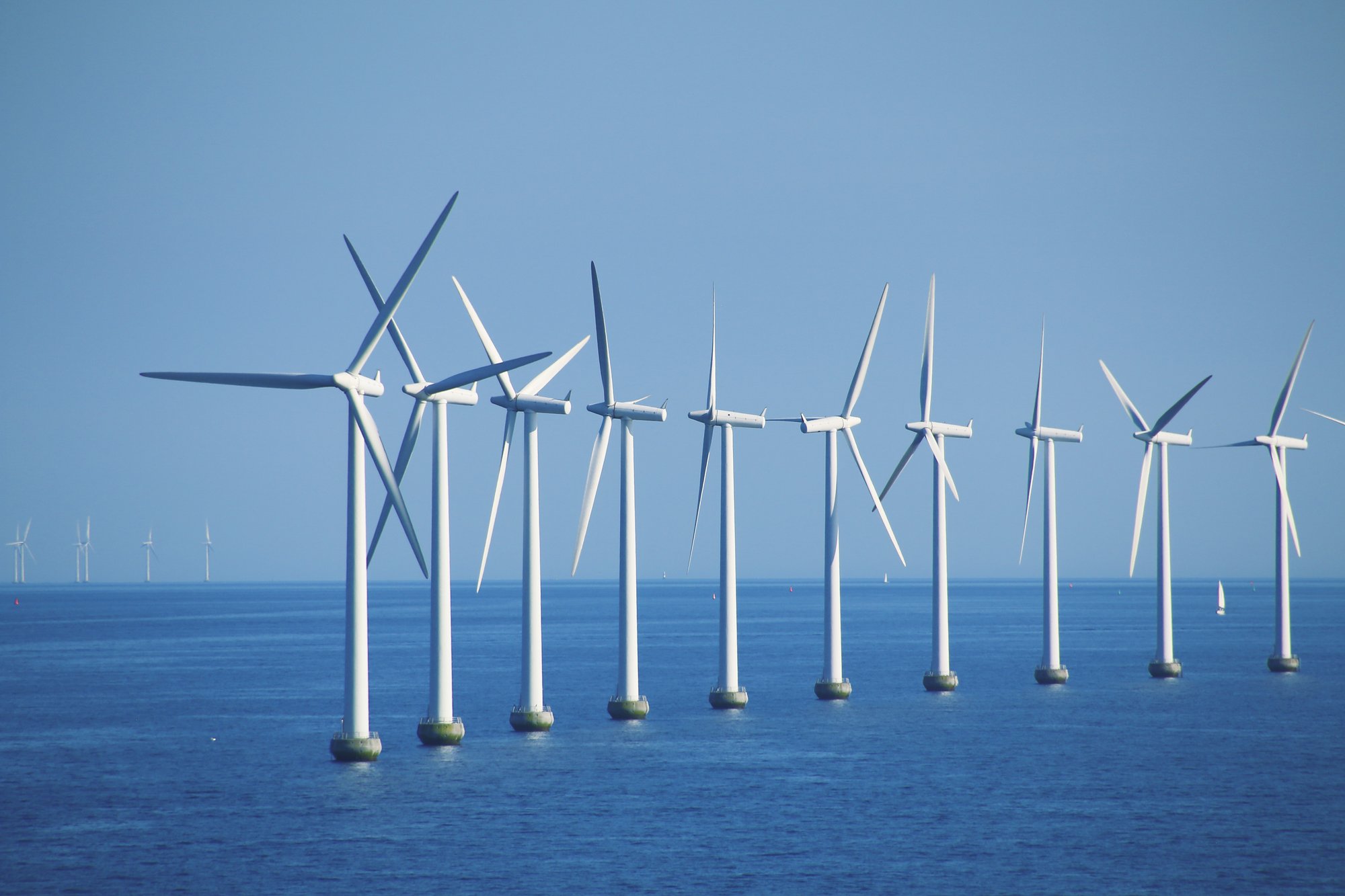
Creating renewable energy
In the energy generation field, our glass is about to be used as cover glass for solar power generation panels.
Regarding glass for solar power generation, our ultra-thin glass will soon be used as a cover glass for solar panels on artificial satellites, where lightweight glass is particularly required. This glass has ultraviolet rays shielding properties, which prevents cell deterioration and contributes to a longer lifespan. It also has potential as substrate glass for perovskite solar cells.

All-solid-state sodium-ion secondary batteries
To store generated energy efficiently and safely, we developed an all-oxide all-solid-state sodium (Na)-ion secondary battery, whose cathode, anode, and solid electrolyte are entirely derived from our proprietary glass-ceramics technology and are firmly integrated. Because all the materials are stable oxides, the battery operates stably even in harsh environments (−40°C to 200°C) and does not pose the risk of fire or toxic gas generation. This is an innovative all-solid-state secondary battery that for storage does not use lithium (Li), for which there are concerns about geographically uneven production and supply. Instead, it uses sodium (Na), which is in plentiful supply.

“A myriad of applications for NEG’s special glass”
Yamazaki “NEG’s company philosophy is to ‘strive to build a brighter future for the world by uncovering the unlimited possibilities of glass for more advanced and creative manufacturing.’ NEG’s strength is to realize glass products with functions that are completely unfathomable to the general public in various ways.”
New challenges to attain the SDGs
This year, NEG formulated the new EGP2028 medium-term business plan. As a new business strategy to attain the SDGs and realize sustainable growth into the future, the business plan focuses on “energy,” “the environment,” “medical care,” and “food,” which are basic to our lives, as the business fields that should be prioritized in the future. Active initiatives are underway along with the sustainability strategy, including carbon neutrality.
As part of its initiatives to pursue the unlimited possibilities of glass, NEG gathers young and spirited employees and asks, “What can you do using glass?” to solicit innovative ideas. The ideas we need are those that will lead to a successful business 30 years ahead. We make steady progress toward the future.
Why not explore new possibilities using glass, a sustainable material derived from the Earth that holds vast potential?