Exploring the Question "What is Glass?"

Fundamental Glass Science Chair Jointly Established by Kyoto University and NEG and the Importance of Basic Research
Glass is not just a transparent material. Many types of special glass which transcend the general image of glass have been developed, such as bendable glass and heat-resistant glass.
Glass can have various functions, properties, and shapes depending on the combination of additives and manufacturing processes. Thanks to ongoing R&D on glass by different organizations and researchers, the scope of glass applications has been expanding to the latest consumer devices and space development equipment, in addition to window glass and tableware, which are familiar products.
However, glass research still has a long way to go. Even modern science cannot give a clear answer to the fundamental question “What is glass?” Finding the answer is the key to unlocking new possibilities of glass. To this end, basic research is indispensable.
It is an important challenge to maintain and develop the environment that underpins glass research. With the number of glass laboratories decreasing in Japan, next-generation researchers must be nurtured, and the research foundation must be reinforced. Against this backdrop, Nippon Electric Glass (NEG) and Kyoto University established the Fundamental Glass Science Chair (an endowed chair) at Kyoto University in April 2023.
This article reports on the outline, significance, and future outlook of basic research on glass along with an interview with Program-Specific Professor Atsunobu Masuno of Kyoto University, who holds the chair.
- Establishment of the Fundamental Glass Science Chair based on the trust method for the first time at Kyoto University
- Basic research to answer the question “What is glass?”
- Current status and challenges of glass research in Japan
- What is the significance of the Fundamental Glass Science Chair?
- Nurturing young researchers through the endowed chair
- Future outlook
Establishment of the Fundamental Glass Science Chair based on the trust method for the first time at Kyoto University
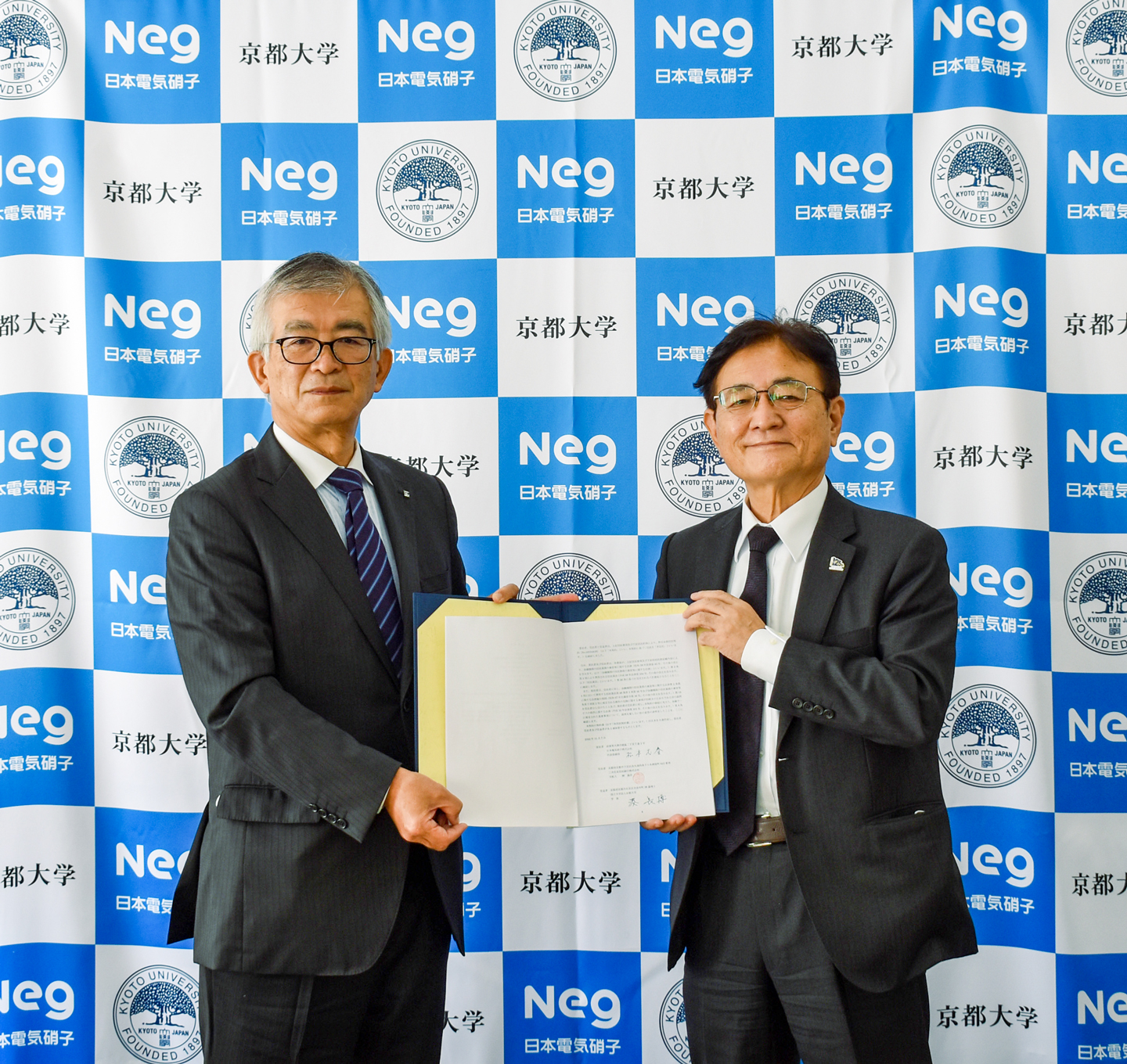

The Fundamental Glass Science Chair was established with the aim of further advancing Japan’s world-leading glass science and technology and nurturing next-generation glass researchers and engineers (press release dated November 7, 2022). NEG provides a stable research environment by contributing one billion yen as initial funding and replenishing an amount spent up to 100 million yen each year.
The chair is held by Program-Specific Professor Atsunobu Masuno of Kyoto University. Research is underway on the following themes.
-
Improvement of the functionality of glass and creation of compositions that impart new functions
-
Prediction of correlation between compositions and physical properties
-
Understanding of glass structure, structural relaxation, glass transition, phase splitting, crystallization, properties of high-temperature melts, etc.
-
Atomic-level structural analysis and measurement technology for physical properties under high temperature and high pressure
-
Development of new processes related to melting, forming, processing, strengthening, etc.

He withdrew, with research guidance approval, from the doctoral course of the Department of Chemistry, Graduate School of Science Division of Chemistry, Kyoto University, in 2004. He worked as a researcher at the Institute for Chemical Research, Kyoto University, aerospace project researcher at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, assistant professor at the Institute of Industrial Science, the University of Tokyo, and associate professor and professor at the Graduate School of Science and Technology, Hirosaki University. He has held his current position since April 2023.
Basic research to answer the question “What is glass?”
In the scientific world, solids with atoms in a regular arrangement are called crystals, while those with atoms in an irregular arrangement are called glass. For example, water turns into ice with a crystalline structure when it is cooled. However, glass is a solid without a crystalline structure, and the majority of its properties remain unknown.
Program-Specific Professor Atsunobu Masuno, who heads the Fundamental Glass Science Chair, takes on the challenge to answer the fundamental question “What is glass?” He succeeded in synthesizing glass with entirely new properties using containerless processing, in which glass is levitated and melted by laser without using a crucible (a heat-resistant container for melting materials, including glass and metal). The analysis found that, in contrast to conventional wisdom, glass has an orderly atomic arrangement, which is the key to demonstrating superb functions.
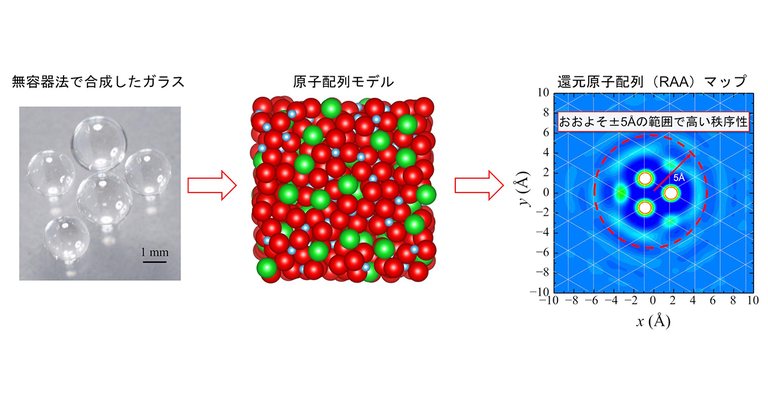
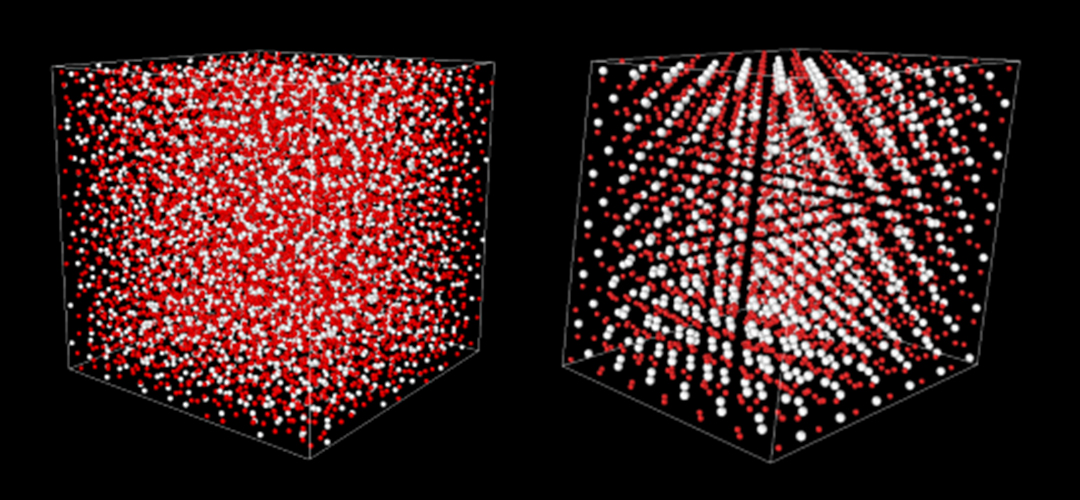
Program-Specific Professor Masuno’s focus extends beyond ground-based research. The professor also participates in a project to produce glass on the Japanese Experiment Module “Kibo” of the International Space Station (ISS). He has been the principal researcher since 2023. He conducts research on highly homogeneous glass and glass with novel structures, which are difficult to achieve on Earth, by using the microgravity environment* in space.
* Microgravity environment: Space is often perceived as gravity-free, but in reality, it is slightly affected by Earth’s gravity. In addition, gravitational force acts between objects (the law of universal gravitation). This is technically referred to as microgravity.
Current status and challenges of glass research in Japan
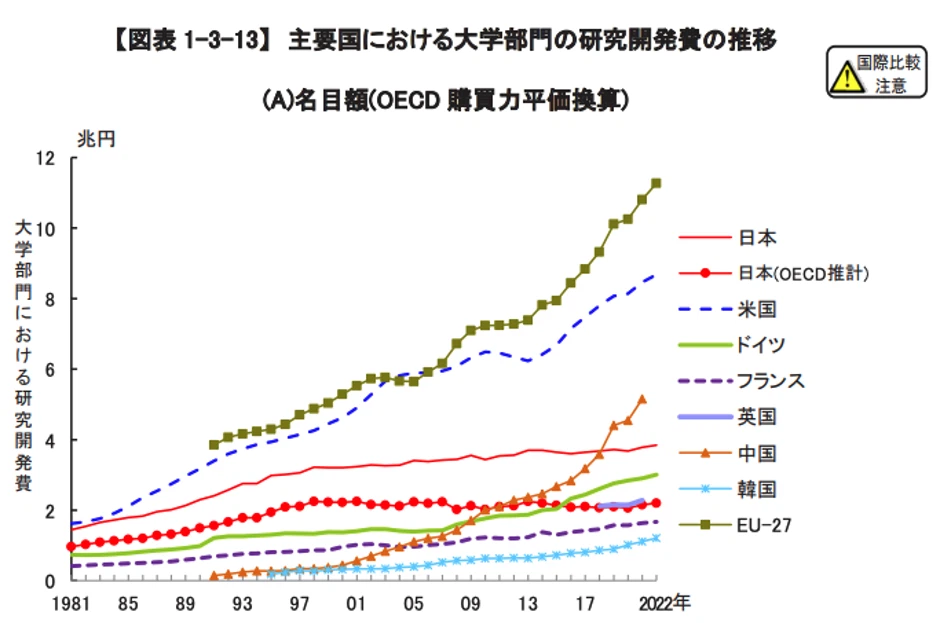
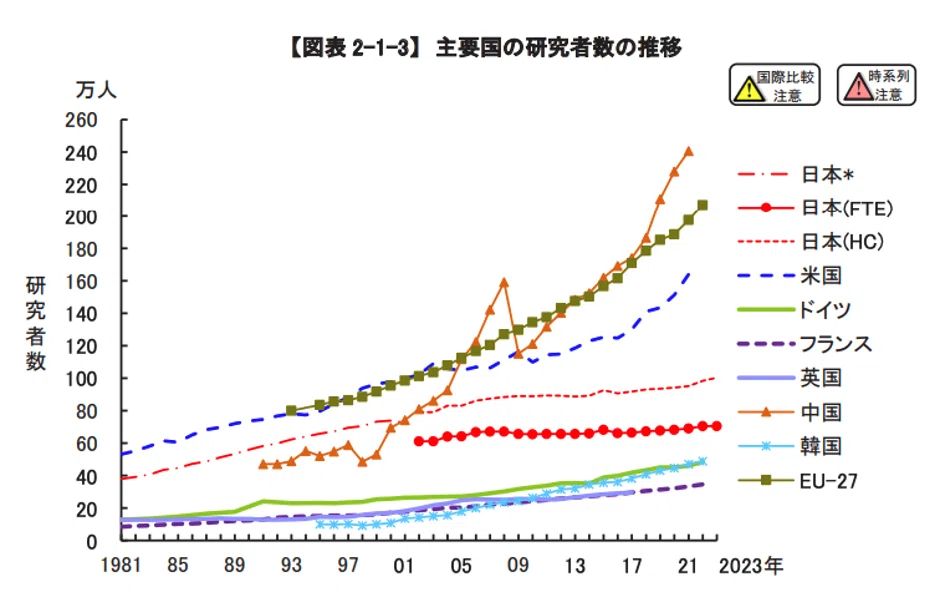
The amount of research expenditures and number of researchers remaining flat at Japanese universities
The graph below, which was created by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, shows the changes in the amount of R&D expenditures and the number of researchers in the university sector in leading countries. The overall amount of research expenditures and number of researchers have remained flat at Japanese universities. Today, Japan is far behind Europe, the U.S., and China.
The environment surrounding glass laboratories in Japan following a similar trend
— What do you think of the current status of glass research in Japan?
Prof. Masuno “The number of glass laboratories at universities has been decreasing gradually. The amount of research expenditures subsidized by the Japanese government has also been decreasing in line with the decrease in the number of laboratories and researchers, leading to fewer new themes and groundbreaking results in the field of glass. We are in a vicious cycle.”
“Meanwhile, there have been great advances in analytical and calculation methods for investigating glass structure, such as the arrangement and bonding state of atoms that make up glass, which were previously unknown. Glass research is entering a new phase. If we produce new results by harnessing such findings, Japan’s glass research will attract attention again and evolve into a major field.”

Prof. Masuno “The Fundamental Glass Science Chair, an endowed chair established by NEG, has had a major impact on academia. Continuous allocation of a generous budget to basic research based on the trust method will help us discover laws and principles which were previously unknown.
It takes considerable time until concrete results are generated within the industry through basic research and applied R&D. However, core-focused research is the source of innovative technologies and products of the future. It is essential to invest from a long-term viewpoint.”
What is the significance of the Fundamental Glass Science Chair?
The Fundamental Glass Science Chair established by NEG at Kyoto University has attracted attention as a new model for ensuring the continuity and stability of basic research of all types. An environment where research can be conducted from a long-term viewpoint without focusing on short-term results is essential for genuine basic research.

― What research are you going to conduct through the chair?
Prof. Masuno “One of my primary missions is to create glass that defies conventional wisdom. This requires establishment of an environment where we can independently analyze glass we produce. To truly understand glass, we must be able to produce glass, measure and analyze its physical properties, and conduct structural analysis by ourselves.”
“What matters in university research is not just to develop new types of glass and measure physical properties but also to elucidate the underlying mechanisms of phenomena. In this context, we must first elucidate glass structure, which remains unknown. Specifically, we plan to introduce a large NMR*1 system within the next few years. We will also actively use large external facilities, including SPring-8.*2 Furthermore, we will establish an environment that enables three-dimensional rendering and analysis of complex atomic arrangements using computer simulations.”
*1 NMR: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. It was previously used for analysis of molecular structures of organic substance. Recently, it has been increasingly used for structural analysis of glass. This analytical technology enables non-destructive and quantitative evaluations.
*2 SPring-8: A large synchrotron radiation facility in Harima Science Garden City in Hyogo Prefecture. It is one of the most powerful synchrotron radiation sources in the world.
― What is the role of university laboratories?
Prof. Masuno “At companies, discussions may often be held from the viewpoint of phenomena, such as creation of new glass and improvement in properties by changing compositions through trial and error. On the other hand, university laboratories, including mine, should focus on establishment of theories to elucidate the mechanisms. Glass is regarded as a material whose structure is not fully understood because, unlike crystals, glass is characterized by a disordered atomic structure. The question is often sidestepped even in modern science of glass. In response to the question “What is glass?” it was only possible to explain the material as “something that is not a crystal.” I hope to properly explain what glass is. I want to deeply understand the principles of glass structure and pursue unlimited possibilities of glass in the truest sense.”」
Nurturing young researchers through the endowed chair
The future of basic research on glass depends on young researchers and engineers, who will be future leaders. The Fundamental Glass Science Chair at Kyoto University not only advances research but also nurtures future leaders of glass research. This is crucial in maintaining and improving the international competitiveness of Japan’s glass research.
― What are your thoughts on nurturing young researchers?
Prof. Masuno “I want to nurture researchers who can handle the entire process, from production to analysis, have a comprehensive view of the material of glass, and establish a shared understanding through discussions with other researchers. The key is measurement and analysis of glass structure, which I explained earlier. Structural analysis of glass requires in-depth understanding of theories and sophisticated measurement skills. The funds for the Fundamental Glass Science Chair will be used properly to establish an environment for advanced structural analysis and develop talent. Active interaction will also be promoted with overseas laboratories that have excellent technologies and theories.

― What is your vision for further stimulating research and increasing the number of researchers?
Prof. Masuno “I expect researchers, after obtaining their doctoral degree, to take active roles in the outside world. Researchers immediately after obtaining their degree have limited experience. However, if they actively spread the appealing aspects of glass research at different universities and research institutes, the buds of glass research will bloom in various areas. I hope that they will establish their own glass laboratories when they become full-fledged researchers.”
Such initiatives are expected to inspire broader interest in glass research among younger generations and attract more talented people to this field.
Future outlook
Program-Specific Professor Masuno has already been promoting research in collaboration with more than 10 research institutions in Japan and overseas. He also discusses comprehensive basic research themes with the Center for Glass Science and Technology of the University of Shiga Prefecture, at which an endowed chair has been established by NEG, and NEG to formulate research plans.
Program-Specific Professor Masuno gave a reassuring message: “In addition to such collaboration, I will promote collaboration with various institutions in Japan and overseas to create one of the large hubs of global glass research.”
Apparently, basic research on glass is low-profile and does not immediately produce visible results. However, it offers profound, infinite possibilities. In fact, glass, which is a familiar material, offers untapped possibilities, and its true nature is yet to be fully elucidated.
NEG will contribute to society by supporting research with a long-term perspective in line with NEG’s company philosophy, “We strive to build a brighter future for the world by uncovering the unlimited possibilities of glass for more advanced and creative manufacturing.”
Note: For the annual report of the Fundamental Glass Science Chair based on the trust method, click/tap here
Reference: NEG's R&D organization