Waste Reduction
Basic Policy
Realizing a recycling-oriented society requires a strong commitment to using resources efficiently by developing internal recycling technologies and by promoting broader societal recycling systems that span the entire product lifecycle from production to consumption and disposal. Following our policy to “internally recycle all solid waste related to the glass business,” we adopted a Waste Business Plan in fiscal 2001 aimed at minimizing and recycling waste generated during manufacturing. The goal is to significantly lower the volume of waste sent to landfills, which has a considerable environmental impact. We are continuing these efforts as part of our ongoing commitment to making the most effective use of resources.
Waste Classification
Waste is categorized into normal waste generated from regular production activities, and bulky construction waste generated from activities such as glass melting furnace maintenance.
These are further divided into four subcategories, with Landfill Waste D being the highest priority for reduction due to its significant environmental impact.

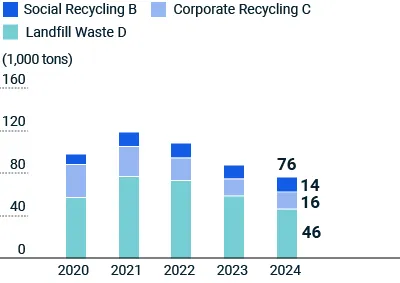
Reduction of Landfill Waste D
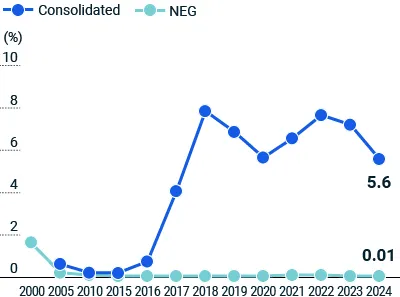
We set annual targets and reduction plans for normal waste (Landfill Disposal D) based on intensity per unit of sales as a percentage of weight (tons of waste/sales weight). In Japan, we set a target to maintain annual waste intensity at 0.1% or lower, and our initiatives to reduce daily waste to the absolute minimum and promote recycling have enabled us to achieve our target every year since 2009. We are also implementing measures to reduce the volume of normal waste from our operations overseas. This is particularly important following the significant increase in waste volume after the acquisition and consolidation of composites business units in the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, and the United States in 2016 and 2017.
In fiscal 2024, we achieved our waste intensity target of 0.1% or lower per unit of production in Japan. In addition, the overall intensity per unit of sales by weight for business divisions in Japan and overseas was 5.6%, a decrease of 22% from the previous fiscal year. In fiscal 2025, we are taking steps to further improve production efficiency and implementing reduction measures aimed at achieving an intensity per unit of production of 3.7%. The Environmental Management Committee is leading the effort by considering measures and reporting on the progress.
Bulky construction waste (Landfill Waste D) is primarily non-recyclable brick from glass furnace repairs.
In fiscal 2017, we converted waste bricks from the Landfill Waste D to the Social Recycling B category by having refractory manufacturers repurpose waste chromium and zirconium bricks as raw materials. This has significantly reduced landfill disposal associated with chromium bricks, a specially controlled industrial waste material. We also sort bricks made of alumina, mullite, and other refractory materials recovered during the repair and dismantling of glass melting furnaces. We engage certified recycling operators to convert recyclable bricks to Social Recycling B materials.
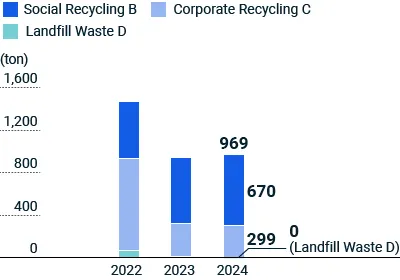
Reduction of Waste Other Than Landfill Disposal D
For waste categorized as Social Recycling B and Corporate Recycling C, we work to reduce emissions, separate materials for reuse, and repurpose waste to incinerate for thermal energy.
In fiscal 2024, we emitted 969 tons of plastic waste from our Japanese factories. Of this, 299 tons were classified as Corporate Recycling C and Landfill Waste D, and 670 tons were reused as Social Recycling B.
Our efforts to reduce and separate waste from our business sites achieved a year-on-year reduction of 12 tons in Corporate Recycling C plastic in fiscal 2024.
We are also continuing efforts to reduce waste at our business sites overseas.
-
Values are retroactively adjusted to from fiscal 2022 due to a change in the waste aggregation method effected in fiscal 2024.
In the Internal Recycling A waste category, we have developed technology to recycle glass raw materials by recovering and reusing grinding sludge, electrostatic precipitator dust, and boric acid dust, which is a primary substance in the gas emissions during molten glass evaporation.
Glass fibers used to reinforce composite materials are coated with an organic surface treatment that protects the fibers and ensures proper adhesion to resins. However, this treatment makes it difficult to recycle waste and scrap generated during manufacturing, leading many glass fiber producers to dispose of it. NEG has developed a proprietary technology that removes and pulverizes the surface treatment agent, allowing the recovered material to be reused as a raw material for glass production.
